Method
In recent years, active research on locusts has revealed the presence of the 4VA of locust attractant pheromone, the Or35 of olfactory receptor, and rutin, which works specifically on locusts. We thought that by combining them, we could solve the locust plague. The following is a description of these substances.
・4-Vinyl anisole (4VA) : attractant pheromone
4VA is a pheromone released from the body and feces of locusts, and it shows attractiveness regardless of the locust's developmental stage, sex, and whether it is a solitary or gregarious phase. It is particularly attractive to locusts in the swarming phase, and the amount of 4VA released increases as the population density increases【2】.
・Or35 : receptor
Or35 is an olfactory receptor specific for 4VA in the antennae of locusts. It is a seven-fold transmembrane protein that depolarizes the cell membrane upon receiving a signal and converts it into an electrical signal. It is also a cell membrane protein that passively transmits cations through the cell membrane when it detects 4VA, and is called a "cation channel"【2】【5】.
・Rutin: locust specific poisons
Rutin is a kind of plant flavonoid (polyphenol) that works as a poison specifically for locusts. When rutin enters the body, locusts produce an excess amount of reactive oxygen species. In response, it activates antioxidant and detoxification enzymes, which require large amounts of energy and thus weaken the locusts and reduce its survival rate【3】.
A series of flows
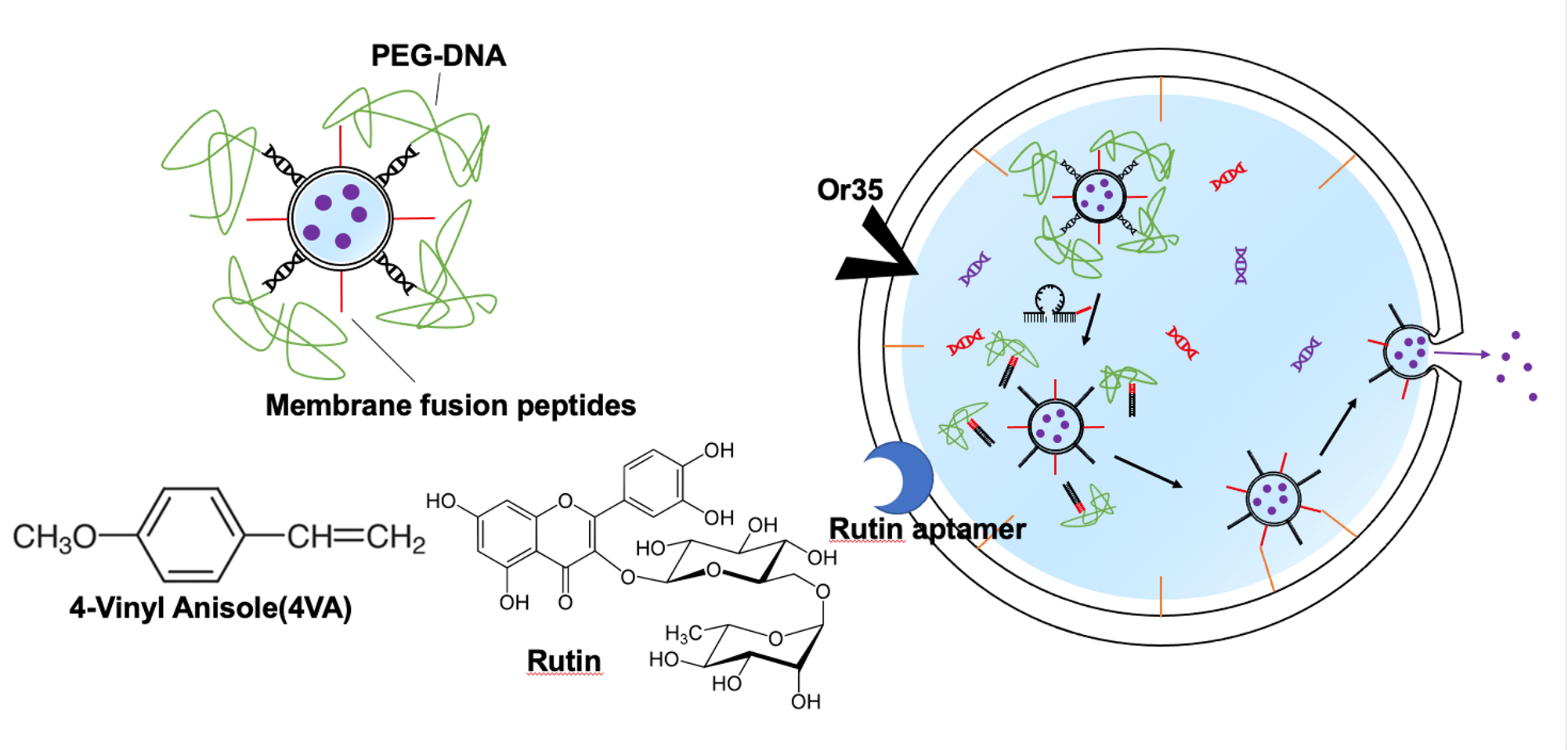
We propose a molecular robot that can release or inhibit the release of rutin by detecting 4VA and rutin. This molecular robot is composed of the inner liposome of several hundred nm and the outer liposome of several μm. Our robot is inspired by the mechanism of synthetic beta cells【1】.
Or35 and rutin aptamers are bound to the outside of the lipid bilayer of Outer liposomes.Potassium ions in the dispersion can permeate into the Outer liposome when Or35 detects 4VA. Membrane fusion peptides are also bound to the inner lipid bilayer.
The outside lipid bilayer of the inner liposome contains the membrane fusion peptides and the Poly Ethylene Glycol(PEG) conjugated double-stranded DNA, and the peptides are protected by PEG-DNA. Rutin is encapsulated in the inner liposome.
The sequence of the rutin release mechanism of the molecular robot is described below.
First, 4VA is detected, and potassium ions permeate into the molecular robot, releasing the input DNA. Next, when the input DNA reaches the threshold, the output DNA is released. The PEG-DNA protecting the membrane fusion peptide is released by the output DNA, which leads to membrane fusion between the Outer and Inner liposomes and the release of rutin.
The sequence of the rutin release inhibition mechanism is described below. First, the concentration of rutin in the dispersion is detected and the input DNA2 is released. Next, Hybridization of the input DNA2 with the input DNA stops the release of output DNA,and prevents further membrane fusion of liposomes and inhibits the release of rutin.
Mechanism
Next, we will explain the detailed mechanisms of the sensors, processors, and actuators in the rutin release and inhibition release of our proposed molecular robot.
Rutin release mechanism
・Sensor


When Or35 detects 4VA, potassium ions in the dispersion permeate into the Outer liposome. A double-stranded DNA consisting of G-rich DNA and input DNA exists in the liposome, and the G-rich DNA reacts with potassium ions to form a G quadruplex. This will narrow the hybridization region with the input DNA and destabilize the binding, resulting in the release of the input DNA.
・Processor
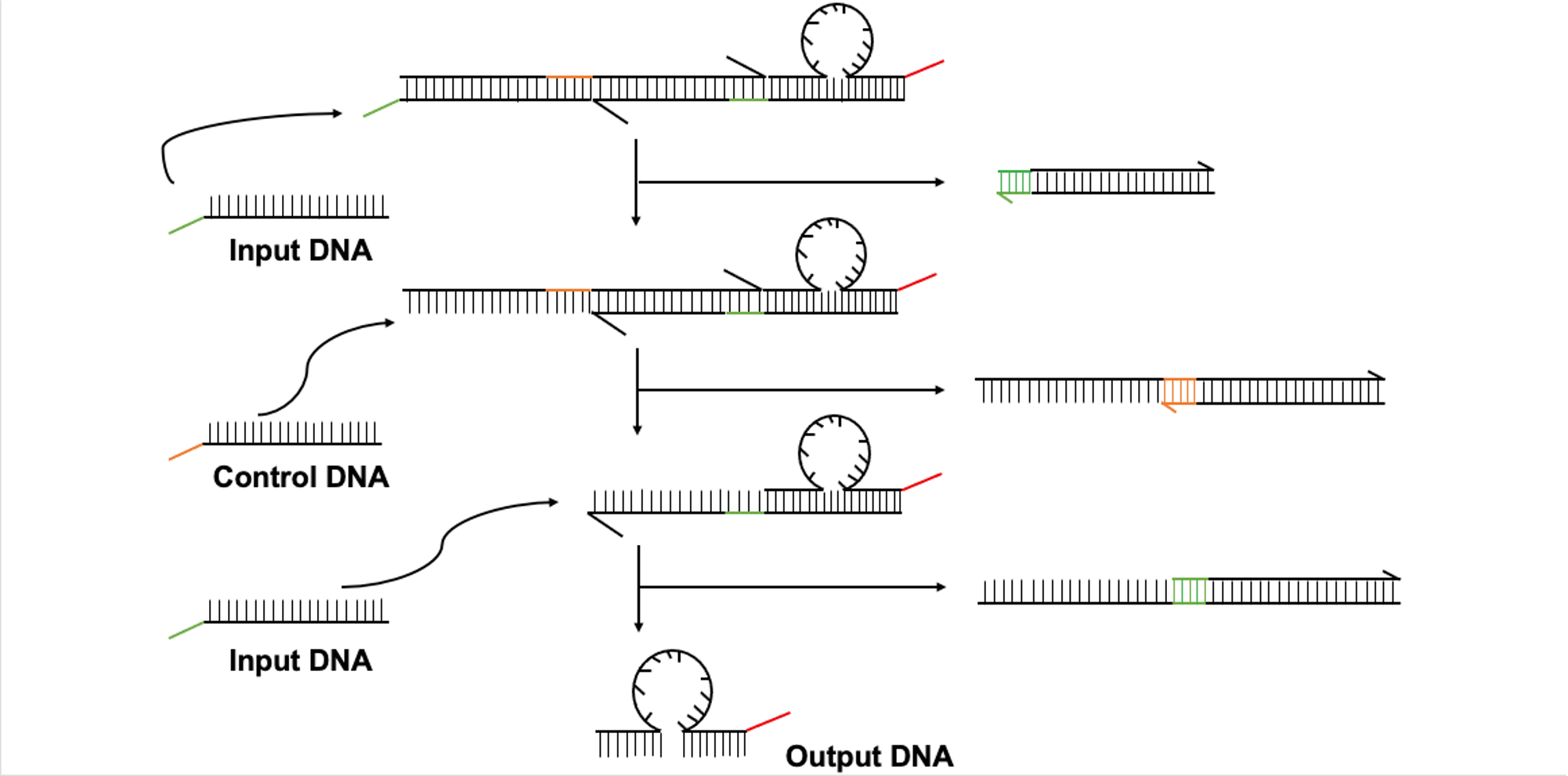
A DNA-based digital logical circuit, Threshold Gate, is used.[4] In the threshold gate, only the gate strand is consumed and no output DNA is released unless a set threshold amount of input DNA is bound.In consequence, the output DNA with a complementary sequence to PEG-DNA is released only when the detected concentration of 4VA exceeds a threshold value.
・Actuator
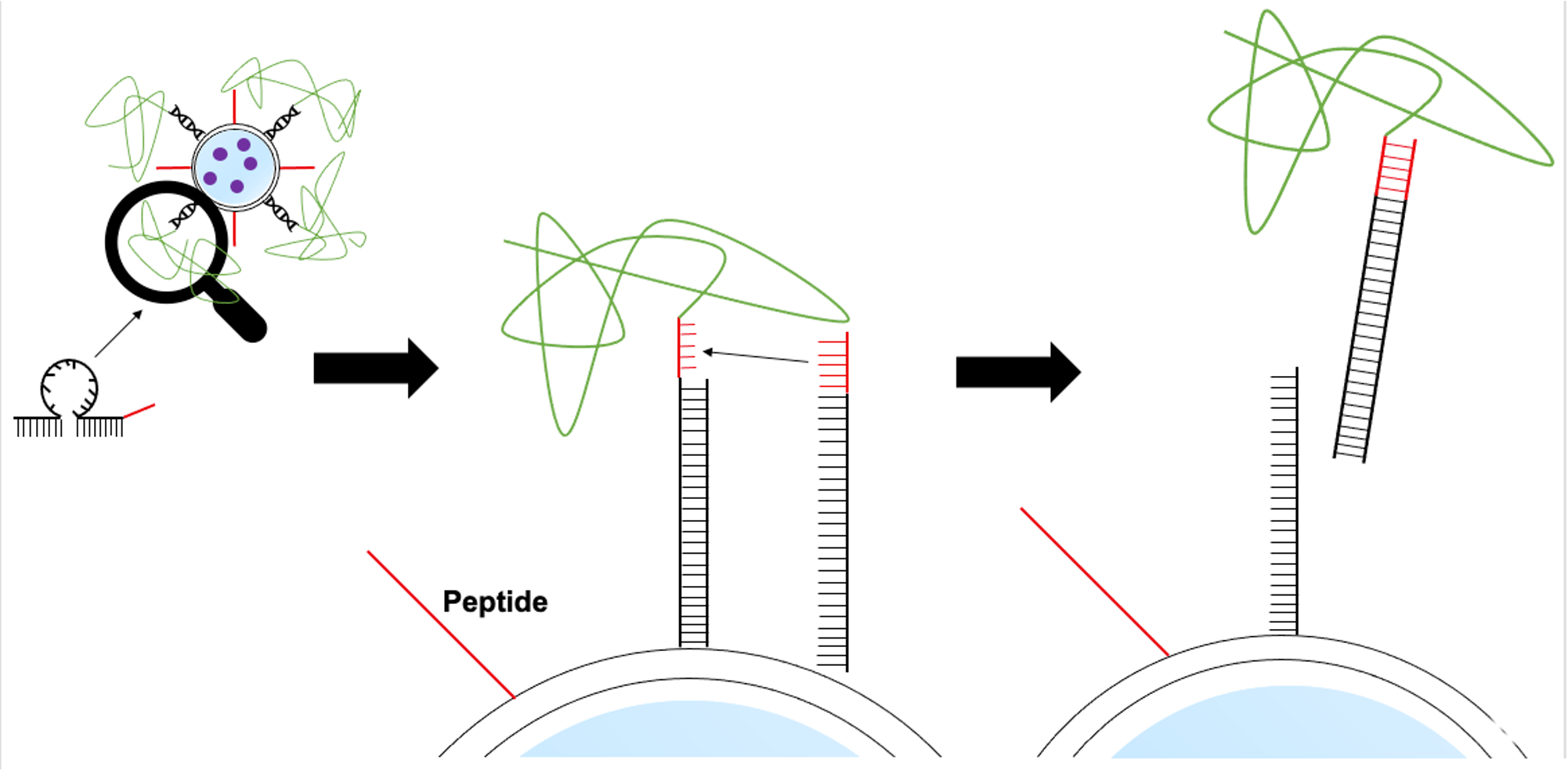
The input DNA2 has a complementary sequence to the input DNA in the rutin release mechanism. In consequence hybridization with the input DNA stops the release of output DNA, and prevents further membrane fusion between inner and outer liposomes and stops the release of rutin.
Inhibition mechanism of rutin release
・Sensor
The rutin aptamer detects the released rutin in the dispersion and releases the input DNA2 into the Outer liposome【6】.
・Actuator
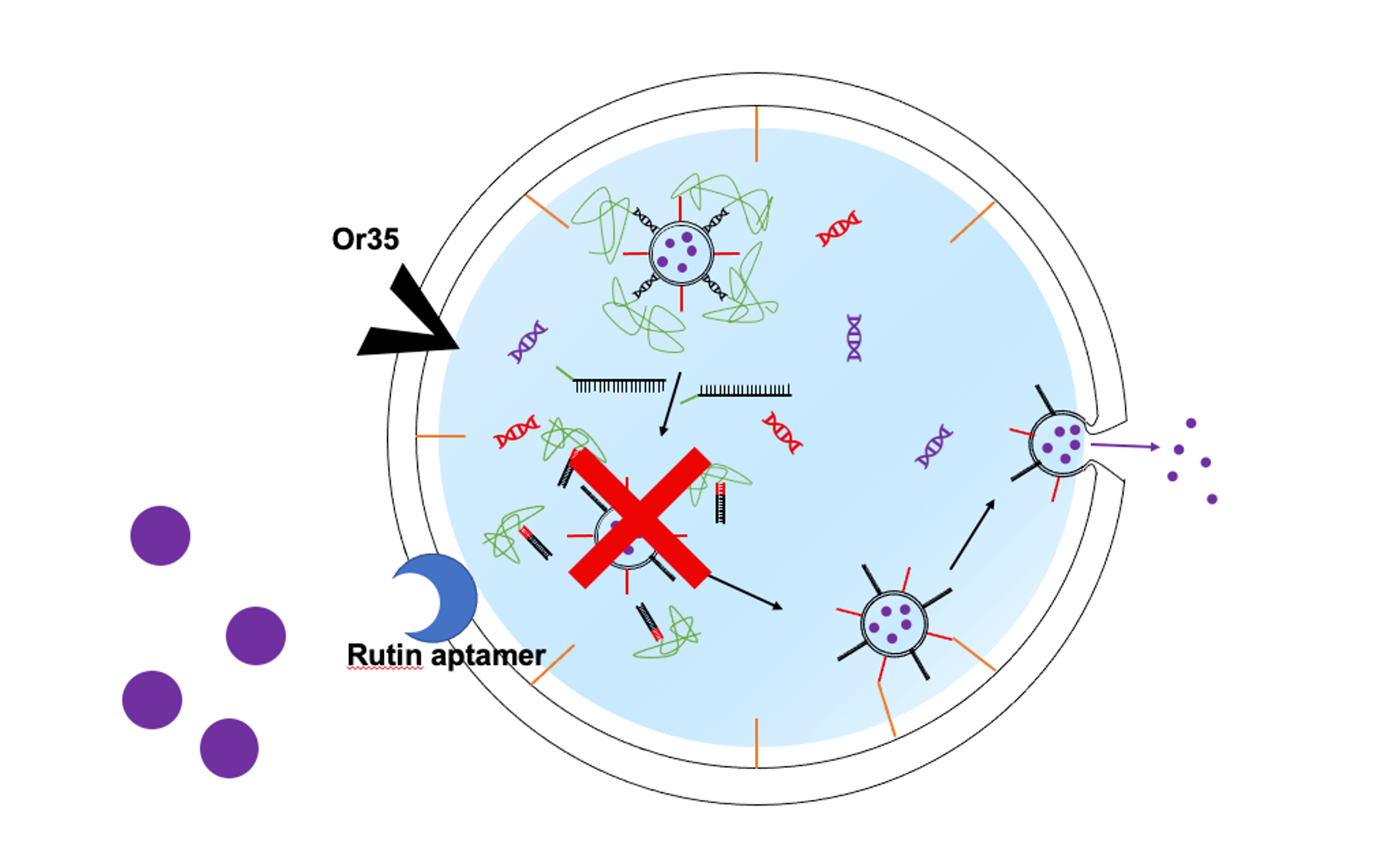
The input DNA2 has a complementary sequence to the input DNA in the rutin release mechanism. In consequence hybridization with the input DNA stops the release of output DNA, and prevents further membrane fusion between inner and outer liposomes and stops the release of rutin.
Reference
[1]Zhaowei Chen, Jinqiang Wang, Wujin Sun, Edikan Archibong, Anna R Kahkoska, Xudong Zhang, Yue Lu, Frances S Ligler, John B Buse & Zhen Gu ,synthetic beta cells for fusion-mediated dynamic insulin secretion. Nat. Chem. Biol., doi:10.1038/nchembio.2511(2017)
【2]Guo, X., Yu, Q., Chen, D. et al. 4-Vinylanisole is an aggregation pheromone in locusts., Nature 584, 584-588 (2020)
[3]Wang, Y., Huang, X., Chang, B.H. et al. The survival, growth, and detoxifying enzyme activities of grasshoppers Oedaleus asiaticus (Orthoptera: Acrididae) exposed to toxic rutin. Appl Entomol Zool 55, 385–393 (2020).
[4]Georg Seelig, et al., Enzyme-Free Nucleic Acid Logic Circuits, Science 314, 1585 (2006).
[5]Nakagawa T, Pellegrino M, Sato K, Vosshall LB, Touhara K., Amino Acid Residues Contributing to Function of the Heteromeric Insect OlfactoryReceptor Complex., PLoS ONE 7(3), (2012): e32372. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032372
[6]Guo Liu, Shan Huang, Xiaochen Liu, Wanzhen Chen, Xin Ma, Shuang Cao, Liping Wang, Lanlan Chen, and Huanghao Yang., DNA-Based Artificial Signaling System Mimicking the Dimerization of Receptors for Signal Transduction and Amplification., Anal. Chem. (2021), 93, 41, 13807-13814
